Mapping and maintenance of global identifiers
As the world becomes increasingly global, financial markets are no longer restricted to their local jurisdictions. To increase interoperability with other jurisdictions around the world in order to remain competitive in this international arena, firms need to be willing and able to adopt more global standards.
By adopting universal international standards, the market is able to meet regulatory demands and improve efficiency, cost and help open up the markets to new entrants with access to a common source of data which ultimately improves liquidity. Also, in order to truly innovate and offer exciting new products and services by applying AI, robotics and machine learning, firms need to efficiently consolidate data from various sources and formats.
ANNA collaborates with other institutions on complementary ISO standards initiatives to service the industry. ISO-standard identifiers have become the common language of financial transactions and processing around the world noted for their characteristics of ethical integrity, commitment to open communications and the continuing involvement of the businesses affected.
ISINs and FISNs
ANNA is the registration authority for two ISO standards: the International Securities Identification Number (ISIN (ISO 6166)) , a code that uniquely identifies a financial or referential instrument, as well as the Financial Instrument Short Name (FISN (ISO 18774)), which provides essential descriptive information about an instrument in the form of a human readable alias.
By putting in place rigorous governance around the development, allocation and sharing of the ISIN and FISN standards, we help facilitate open, transparent markets with no barriers to access, while protecting the integrity of the standard. As a result, ISIN has become the recognised global standard for unique identification for all types of financial instruments, helping to connect and protect global markets.
For information about specific identifiers and how they are assigned, please click on the tabs below.
International Securities Identification Number (ISIN)
The International Securities Identification Number (ISO 6166) is the recognised global standard for unique identification for all types of financial and referential instruments. ISINs are used to identify most types of financial instruments, including equity, debt, derivatives and indices.
Growth of ISINs as the industry standard
Because ISIN has been developed by the industry, for the industry, and under rigorous processes established by the International Organization for Standardization, it quickly became the common language of financial instruments and processing around the world. The impact of ISO-identifiers has been significant in helping to reduce the time, cost and risk of cross-border transactions. Additionally, revisions are subject to ongoing governance processes to ensure the integrity of the identifier is protected.
The structure of an ISIN
The ISIN code consists of a total of 12 characters as follows:
- The first two characters are taken up by the alpha-2 country code as issued in accordance with the international standard ISO 3166 of the country where the issuer of securities, other than debt securities, is legally registered or in which it has legal domicile. For debt securities, the relevant country is the one of the ISIN-allocating National Numbering Agency. In the case of depository receipts, such as ADRs, the country code is that of the organisation that issued the receipt, rather than instead of the one that issued the underlying security;
- The next nine characters are taken up by the local numbering code of the security concerned. Where the national number consists of fewer than nine characters, zeros are inserted in front of the number so that the full nine spaces are used;
- The final character is a check digit computed according to the modulus 10 “Double-Add-Double” formula;
For ISINs of OTC derivatives, which will be allocated by a single global numbering agency, the initial two digits will use a custom “EZ” code. The ISIN will be generated on a de novo basis, with no reference to previous or other codes.
Who issues the ISIN
In the case of securities, other than debt securities, in jurisdictions where a NNA recognised by ANNA operates, this organisation issues the ISIN for securities if the issuer is registered or domiciled in the country where the NNA operates. For debt securities, the NNA that issues the ISIN is either one of the international securities clearing organisations or the responsible NNA in accordance with ISO 6166.
In the case of those countries where no NNA exists, a substitute agency allocates the number. Read more.

Financial Instrument Short Name (FISN)
Important update: Since July 1 2017, the FISN is globally assigned concurrently with the ISIN (ISO 6166) and CFI (ISO 10962) at the time of issuance of a new financial instrument.
FISN: Standardising short names of financial instruments
The new standard for the Financial Instrument Short Name (ISO 18774) has been developed by ISO Work Group WG14 to provide a consistent and uniform approach to standardize short names and descriptions for financial instruments. The standard was approved by ballot in September 2014.
Unlike other ISO-standard financial instrument identification codes, the FISN is not meant to be machine-readable, but to provide a short format for essential information about a security for human use.
Current Use of FISNs
Most financial institutions use some sort of internal short name to describe and/or identify a financial instrument for reporting, trading, account statements, etc. Prior to the FISN being made available globally, some financial institutions had to generate this short name themselves, often involving high manual effort.
The FISN standard not only reduces this effort but also enables better communication between the financial institutions and their clients. The FISN is unique as it is unlikely that the combination of issuer name and abbreviated issue description would appear twice.
The structure of the FISN
The ISO 18774 standard incorporates the issuer short name and the abbreviated characteristics for the financial instrument. It has a maximum length of 35 alphanumeric characters. The FISN is composed of:
- “/” as the delimiter between issuer name and instrument description;
- An issuer name with a maximum length of 15 alphanumeric characters. To ensure uniformity, the same issuer short name should be used for different financial instruments of the same issuer;
- Exception: in the case of CIVs (Collective Investment Vehicles) issuer name might be longer;
- An instrument description with a maximum length of 19 alphanumeric characters, assuming that the available length of the issuer name has been fully used. In the event that all the 15 characters have not been used in the issuer short name, the remaining space may be used to describe the characteristics of the financial instrument.
Abbreviation List
The official abbreviation list as maintained by ANNA as Registration Authority can be found here.

Classification of Financial Instruments (CFI)
Important update: Since 1 July 2017, the revised CFI (ISO 10962) and the FISN (ISO 18774) are globally assigned with the ISIN at the time of issuance of a new financial instrument.
CFIs – providing consistency
The CFI code has been developed to address a number of problems which have concerned the financial community in the past years. Among others the following problems have affected the financial community:
- Lack of consistent and uniform approach to grouping financial instruments
- Use of similar terminology for instruments having significantly different features in the different countries
- Inability to group securities in a consistent manner leading to reports of holdings being categorised differently.
The benefits of the new code are:
- Definition and description for an internationally valid system to classify financial instruments
- Provision of a set of codes to be used by all market participants in an electronic data process (EDP) environment and permission of electronic communication between participants
- Improved understanding of the characteristics of financial instruments will lead to a better understanding by investors.
CFI Status and references to CFI codes
With the version of ISO 10962 published in May 2021 the CFI codes being part of previous standard versions have now been externalized. SIX Financial Information has been appointed by ISO as Maintenance Agency and is publishing the recent versions of all CFI codes on their website in Excel format: https://www.six-group.com/en/products-services/financial-information/data-standards.html#scrollTo=maintenance-agency
As the maintenance agency, SIX is responsible for managing the modifications and enhancements of the code list. They are also responsible for publishing updates in a human- and machine-readable data formats like spreadsheets, pdf, csv, json-lD, ttl.
ISO 10962 standard as well as all other ISO standards can be bought from either ISO (https://www.iso.org/standard/81140.html?browse=tc ) or from the local standards bodies of ISO of TC68/SC8: https://www.iso.org/committee/6534796.html?view=participation ISO standards are copyright protected.

Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs): ISIN to LEI mapping initiative
On 4th April 2019, ANNA and the Global Legal Entity Identifier Foundation (GLEIF) launched a new initiative to link International Securities Identification Numbers (ISINs) and Legal Entity Identifiers (LEIs). The initiative has been created to help improve transparency of exposure by linking the issuer and issuance of securities.
This global project will map new and legacy ISINs to their corresponding LEIs, of those NNAs who have joined the initiative. By linking the two ISO standards together, firms will be able to aggregate the data required to gain a clear view of their securities exposure within a given issuer and its related entities. The ISIN-to-LEI mapping table is freely available to all without restriction on both the GLEIF and ANNA websites.
As the registration authority for the ISIN, ANNA has been responsible for evolving and promoting the ISIN standard through its work and collaboration with members, regulators and the industry at large. As a result, today ISINs are issued in more than 200 jurisdictions worldwide, enabling global cross-border trading and improved transparency. This initiative underlines ANNA’s commitment and mission to promote the use of standards, including the two ISO standards used in this initiative: ISIN (ISO 6166) and LEI (ISO 17442). Watch this video to find out more about the LEI.
Access to the ISIN to LEI Mapping files are available on the GLEIF Website.
ISIN:LEI Mapping Initiative Participating NNAS:
| National Numbering Agency | Country | Jurisdiction | Additional Jurisdictions Covered |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASX Limited | Australia | AU | |
| Oesterreichische Kontrollbank Aktiengesellschaft (OeKB) | Austria | AT | |
| Bahrain Clear Company B.S.C. | Bahrain | BH | |
| The Republican Unitary Enterprise - The Republican Central Securities Depository | Belarus | BY | |
| SIX Financial Information Belgium S.A./N.V. | Belgium | BE | |
| Dutch Caribbean Securities Exchange NV | Curacao | CW | |
| Centrální depozitář cenných papírů, a.s. - Central Securities Depository | Czech Republic | CZ | |
| VP Securities A/S | Denmark | DK | |
| Euroclear France | France | FR | |
| WM Datenservice | Germany | DE | AD, BA, EU, FO, GA, GI, IQ, LR, MO, MW, NA, RW, SM, VU |
| Hellenic Central Securities Depositary, S.A. | Greece | GR | |
| The Irish Stock Exchange trading as Euronext Dublin | Ireland | IE | |
| Banca d´Italia | Italy | IT | |
| Tokyo Stock Exchange, Inc. | Japan | JP | |
| Nasdaq CSD SE | Latvia | LV | EE, IS, LT |
| Malta Stock Exchange PLC | Malta | MT | |
| Euroclear Nederland | Netherlands | NL | |
| Central Securities Clearing System Plc. | Nigeria | NG | |
| Verdipapirsentralen ASA | Norway | NO | |
| Krajowy Depozyt Papierów Wartościowych SA (KDPW SA) | Poland | PL | |
| Interbolsa - Sociedade Gestora de Sistemas de Liquidacao e de Sistemas Centralizados de Valores Mobiliarios, S.A. | Portugal | PT | |
| Depozitarul Central S.A. (Romanian Central Depository) | Romania | RO | |
| KDD Central Securities Clearing Corporation | Slovenia | SI | |
| JSE Ltd | South Africa | ZA | |
| Comisión Nacional del Mercado de Valores (CNMV) | Spain | ES | |
| Euroclear Sweden AB | Sweden | SE | |
| SIX Financial Information Ltd | Switzerland | CH | LI |
| Istanbul Takas ve Saklama Bankası A.S.- Takasbank | Türkiye | TR | |
| Uganda Securities Exchange Ltd | Uganda | UG | |
| London Stock Exchange Plc | United Kingdom | GB | GG, IM, JE |
| CUSIP Global Services | United States | US | AG, BM, BS, BZ, GD, KY, LC, MH, PH, PR, TT, VC, VG |
Codes for exchanges and market identification (MIC)
The Market Identifier Code (MIC) (ISO 10383) specifies a universal method of identifying exchanges, trading platforms and regulated or non-regulated markets as sources of prices and related information in order to facilitate automated processing. ISO has appointed SWIFT as the Registration Authority for ISO 10383.
As each National Numbering Agency is deemed the best placed entity to monitor and track developments in their respective jurisdiction, assistance in the coordination of the current MIC list maintained by the MIC Registration Authority is deemed an important element of the NNA function in that market. As the importance of using MIC increases with the continuing evolution towards security processing automation, each NNA is requested to monitor developments in their market and if there are changes, advises the exchange/trading platform and asks them to inform the MIC Registration Authority via the MIC website (www.iso10383.org). It is important to identify any changes that have a direct impact on the accuracy of the MIC list the Registration Authority maintains – such as the addition of new exchanges and/or trading platforms in their market.
The current MIC codes, which are updated on a monthly basis, are available from the following website.
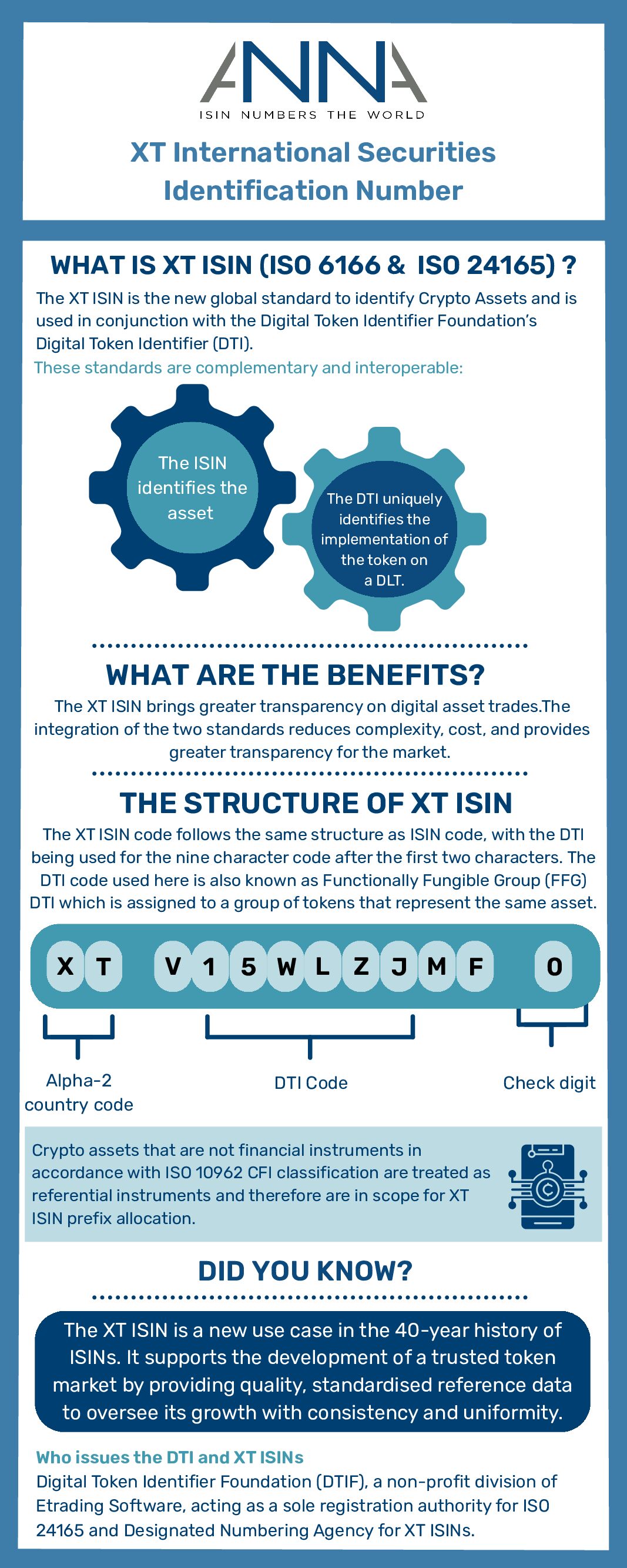
DTI ISO 24165 XT-ISIN
DTIs XT-ISINs are issued and maintained by The Digital Token Identifier Foundation (DTIF), a non-profit division of Etrading Software, a financial technology firm with a mission of solving market-wide problems by building market infrastructures for the new digital economy. With the aim of increasing transparency in the digital asset space through the creation of a core reference data set based on open data principles and available as a public good, DTIF’s mission is to provide the golden source reference data for the unique identification of digital tokens based on ISO’s new standard for digital assets, ISO 24165.